In the realm of medical science, human blood cell typing POGIL answers play a pivotal role in ensuring compatibility for blood transfusions and organ transplantation. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of blood typing, unraveling the significance of the ABO blood group system and the Rh factor, while elucidating the techniques employed for blood cell typing and their clinical applications.
The POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) approach transforms science education, empowering students to actively engage in the learning process. This guide provides a step-by-step roadmap for conducting a POGIL activity on human blood cell typing, complete with examples of worksheets and activities suitable for classroom implementation.
Blood Typing
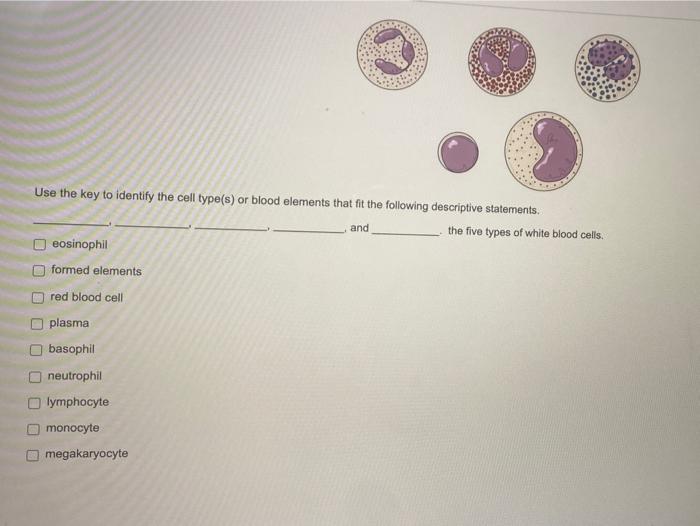
Blood typing is a process that determines the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. These antigens are inherited and play a crucial role in blood compatibility, affecting the success of blood transfusions and organ transplants.
The ABO blood group system is the most widely recognized blood typing system. It classifies blood into four main groups: A, B, AB, and O. Each blood group is defined by the presence or absence of two antigens, A and B.
People with type A blood have only A antigens, those with type B blood have only B antigens, those with type AB blood have both A and B antigens, and those with type O blood have neither A nor B antigens.
Another important blood group system is the Rh factor. The Rh factor is an antigen that can be present or absent on red blood cells. People who have the Rh factor are Rh-positive, while those who do not have the Rh factor are Rh-negative.
Human Blood Cell Typing
Human blood cell typing is the process of determining the blood group of an individual. This information is essential for ensuring compatibility in blood transfusions and organ transplants.
There are two main techniques used for blood cell typing: agglutination and flow cytometry.
- Agglutinationis a process that uses antibodies to clump together red blood cells that have specific antigens. By observing the pattern of agglutination, the blood type can be determined.
- Flow cytometryis a process that uses lasers to measure the size and fluorescence of individual cells. This information can be used to determine the blood type and other characteristics of the cells.
Blood cell typing has a wide range of clinical applications, including:
- Blood transfusions: Blood cell typing is essential for ensuring that blood transfusions are compatible. If a patient receives blood that is not compatible with their blood type, it can lead to a transfusion reaction, which can be life-threatening.
- Organ transplantation: Blood cell typing is also important for organ transplantation. If an organ is transplanted from a donor who is not compatible with the recipient’s blood type, it can lead to rejection of the organ.
POGIL Activities: Human Blood Cell Typing Pogil Answers
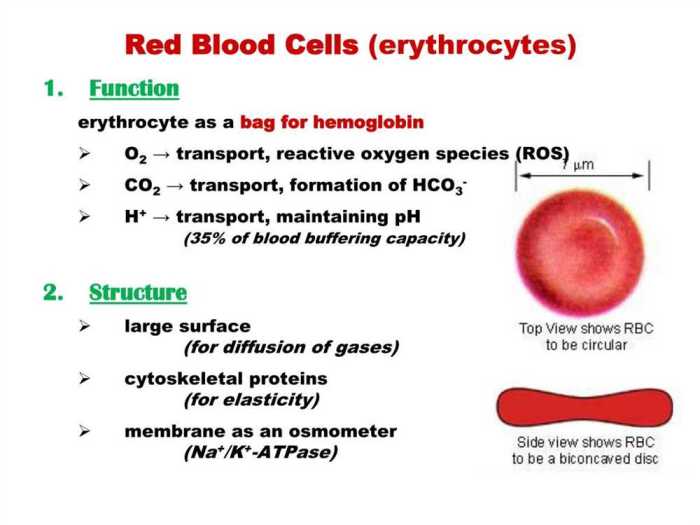
POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) is a science education approach that emphasizes student-centered learning and inquiry-based instruction.
A POGIL activity on human blood cell typing would typically involve the following steps:
- Introduction: The teacher introduces the topic of blood cell typing and its importance in medical applications.
- Exploration: Students work in small groups to explore the different blood group systems and the techniques used for blood cell typing.
- Model development: Students develop a model that explains the inheritance of blood group antigens and the principles of blood cell typing.
- Application: Students apply their knowledge of blood cell typing to solve real-world problems, such as determining the compatibility of blood transfusions or organ transplants.
POGIL activities can be a valuable tool for teaching human blood cell typing because they allow students to actively engage with the material and develop a deeper understanding of the topic.
Data Analysis and Interpretation

The analysis and interpretation of blood cell typing data is essential for making informed decisions about patient care.
When analyzing blood cell typing data, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The patient’s blood type: The patient’s blood type must be known in order to determine the compatibility of blood transfusions or organ transplants.
- The donor’s blood type: If a blood transfusion is necessary, the donor’s blood type must be compatible with the patient’s blood type.
- The presence of antibodies: The presence of antibodies in the patient’s blood can affect the compatibility of blood transfusions or organ transplants.
By carefully analyzing and interpreting blood cell typing data, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care and ensure the safety of blood transfusions and organ transplants.
FAQ
What is the significance of blood typing?
Blood typing determines compatibility for blood transfusions and organ transplantation, ensuring the safe exchange of blood components between individuals.
How does the ABO blood group system work?
The ABO blood group system classifies blood into four types (A, B, AB, and O) based on the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells.
What is the role of the Rh factor in blood compatibility?
The Rh factor is an antigen present on red blood cells in Rh-positive individuals. Compatibility for blood transfusions and organ transplantation requires matching the Rh factor between donor and recipient.
How is blood cell typing performed?
Blood cell typing involves techniques such as agglutination and flow cytometry to detect the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells.
What are the clinical applications of blood cell typing?
Blood cell typing finds applications in blood transfusions, organ transplantation, prenatal testing, and forensic investigations.