Elige el pretérito o el imperfecto para completar la historia. – Choosing the Preterite or Imperfect Tense to Complete the Story, the narrative unfolds in a compelling and distinctive manner, drawing readers into a story that promises to be both engaging and uniquely memorable.
The preterite and imperfect tenses are two essential tools for Spanish language learners. They are used to describe past events and actions, but they each have their own unique set of rules and uses. In this article, we will explore the differences between the preterite and imperfect tenses and provide some tips on how to choose the correct tense for any given situation.
Usage of the Preterite Tense

The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions that occurred at a specific point in time in the past. It conveys a sense of finality and a clear endpoint.
Formation of Regular and Irregular Preterite Verbs, Elige el pretérito o el imperfecto para completar la historia.
- Regular verbs:Drop the -ar, -er, or -ir ending and add -ó, -ió, or -ió.
- Irregular verbs:Have unique preterite forms that must be memorized.
Usage of the Imperfect Tense
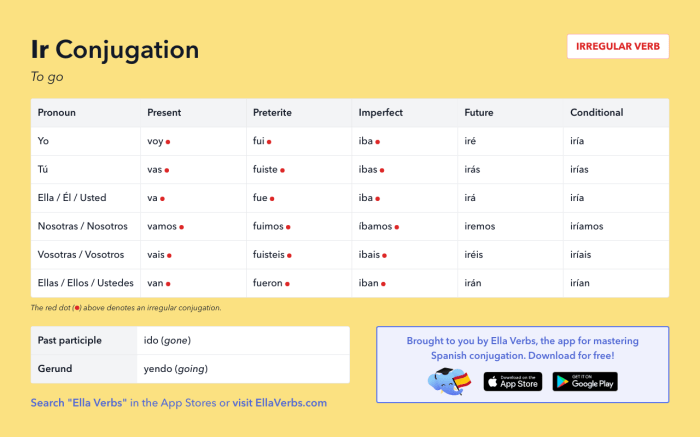
The imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or habitual actions that occurred in the past. It creates a sense of continuity and duration, often without a clear endpoint.
Formation of Regular and Irregular Imperfect Verbs
- Regular verbs:Drop the -ar, -er, or -ir ending and add -aba, -ía, or -ía.
- Irregular verbs:Have unique imperfect forms that must be memorized.
Choosing Between the Preterite and Imperfect Tenses: Elige El Pretérito O El Imperfecto Para Completar La Historia.

The choice between the preterite and imperfect tenses depends on the context:
- Preterite tense:Completed actions with a clear endpoint.
- Imperfect tense:Ongoing or habitual actions, background information, or setting the scene.
Examples of Preterite and Imperfect Tense Usage

| Tense | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Preterite | Ayer, fui al parque. | Yesterday, I went to the park. |
| Imperfect | Cuando era niño, jugaba en el parque todos los días. | When I was a child, I played in the park every day. |
The preterite tense conveys a completed action that happened at a specific time, while the imperfect tense describes an ongoing or habitual action that occurred over a period of time.
FAQ Overview
What is the difference between the preterite and imperfect tenses?
The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions that happened at a specific point in time. The imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or habitual actions that happened in the past.
How do I choose the correct tense?
To choose the correct tense, you need to consider the context of the sentence. If the action is completed, use the preterite tense. If the action is ongoing or habitual, use the imperfect tense.
Can I use both tenses in the same sentence?
Yes, you can use both tenses in the same sentence to create a more complex and nuanced description of past events.