Classify each of the following according to its functional group – Functional groups are the key to understanding the properties and reactivity of organic compounds. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of functional groups, their classification methods, and their significance in determining the behavior of organic molecules.
By delving into the concept of functional groups, we unlock the ability to categorize organic compounds based on their chemical structure and predict their physical and chemical properties. This knowledge empowers scientists and researchers in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental monitoring.
Functional Groups: Classify Each Of The Following According To Its Functional Group
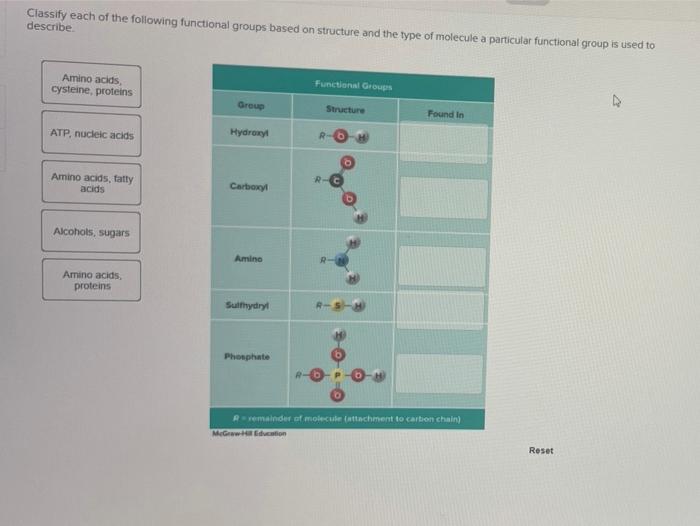
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within a molecule that determine its chemical properties and reactivity. They are responsible for the characteristic behavior and applications of organic compounds.
Common Functional Groups
- Alcohols (R-OH)
- Aldehydes (R-CHO)
- Ketones (R-CO-R’)
- Carboxylic acids (R-COOH)
- Esters (R-COOR’)
- Amides (R-CONH2)
- Amines (R-NH2)
- Alkenes (R-CH=CH-R’)
- Alkynes (R-C≡C-R’)
- Aromatic rings (R-C6H5)
Classification of Compounds
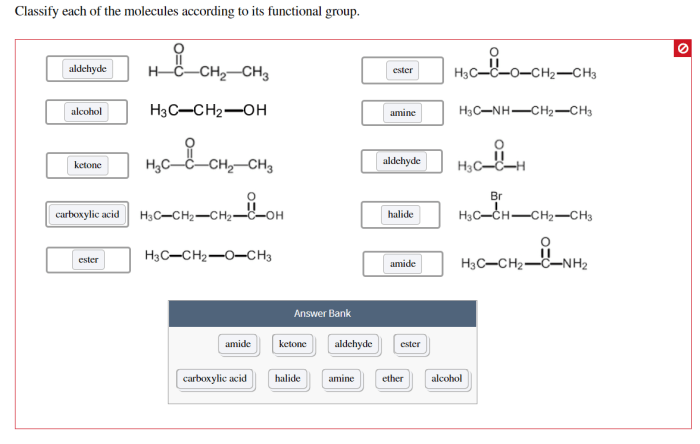
Organic compounds can be classified based on their functional groups using various methods, including the IUPAC nomenclature system.
Classification by Functional Group
| Compound | Functional Group |
|---|---|
| Ethanol | Alcohol |
| Acetic acid | Carboxylic acid |
| Propane | Alkane (no functional group) |
| Butanone | Ketone |
| Benzene | Aromatic ring |
Examples and Properties
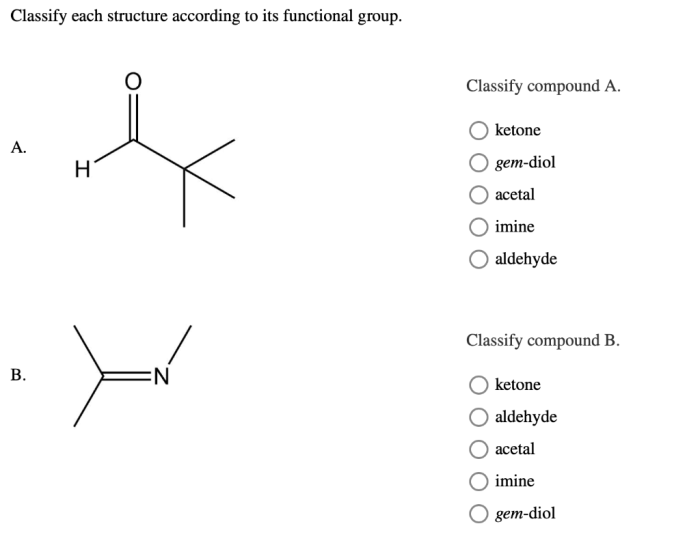
Alcohols
Alcohols contain a hydroxyl group (-OH). They are polar and can form hydrogen bonds, resulting in higher boiling points compared to alkanes. Alcohols are common solvents and can be used in the production of fuels, beverages, and pharmaceuticals.
Carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (-COOH). They are acidic and can react with bases to form salts. Carboxylic acids are used in the production of food, pharmaceuticals, and plastics.
Applications and Significance
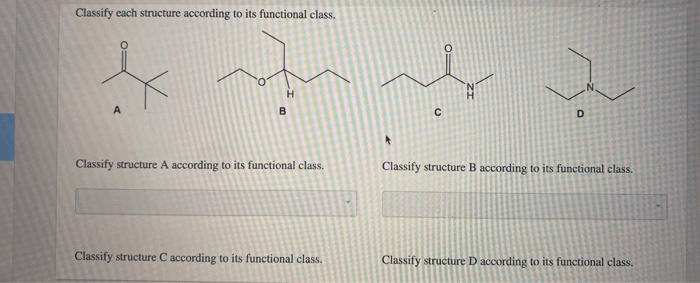
Pharmaceuticals, Classify each of the following according to its functional group
Functional groups play a crucial role in drug discovery and development. Specific functional groups can interact with target molecules in the body, leading to therapeutic effects. For example, the hydroxyl group in alcohols can form hydrogen bonds with polar groups in proteins, while the amine group in amides can participate in covalent bonding.
Materials science
Functional groups influence the properties of materials. For instance, the presence of hydroxyl groups in polymers can enhance their water solubility and biocompatibility, making them suitable for biomedical applications.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the significance of functional groups in organic chemistry?
Functional groups are the primary determinants of the properties and reactivity of organic compounds. They dictate the physical and chemical behavior of molecules, influencing their solubility, boiling point, and reaction pathways.
How are organic compounds classified based on functional groups?
Organic compounds are classified into various functional group families, including alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines. Each family possesses a unique set of functional groups that impart characteristic properties to the compounds.
What are some examples of functional groups and their associated properties?
The hydroxyl group (-OH) in alcohols contributes to their polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds. The carbonyl group (C=O) in aldehydes and ketones is responsible for their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions. The carboxylic acid group (-COOH) imparts acidity to compounds, while the amine group (-NH2) confers basicity.