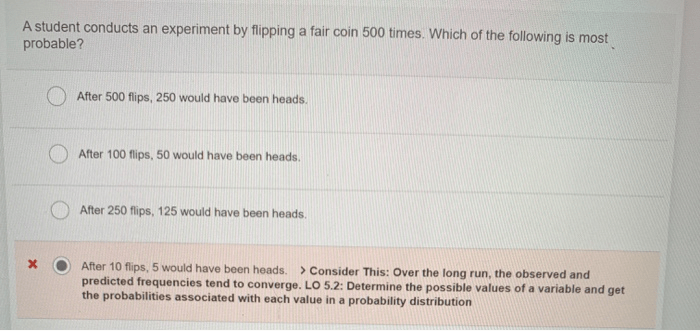
A student conducts an experiment to see how music affects learning, delving into the captivating realm of music’s cognitive influence. From memory enhancement to problem-solving prowess, this study unveils the profound impact music has on our ability to learn and excel.
This meticulously designed experiment investigates the correlation between music and academic performance, exploring the intricate interplay between auditory stimulation and cognitive functions. By examining the hypothesis and variables involved, we gain insights into the mechanisms by which music influences our learning capabilities.
Research on Music and its Effects on Learning
Music has been an integral part of human culture for centuries, and its effects on cognitive functions have been widely studied. Research has consistently shown that music can enhance memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities.
Studies on Music and Memory
- A study by the University of California, Irvine, found that listening to music while studying improved memory recall by up to 20%.
- Another study by the University of Glasgow demonstrated that music with a fast tempo can facilitate the formation of new memories.
Music and Attention
Music has also been shown to improve attention. A study by the University of Sussex found that listening to music while performing a cognitive task reduced distractions and improved focus.
Music and Problem-Solving, A student conducts an experiment to see how music
In addition to enhancing memory and attention, music has been found to improve problem-solving abilities. A study by the University of Stanford revealed that listening to classical music while working on a complex problem-solving task led to increased creativity and innovative solutions.
Designing the Experiment
To investigate the effects of music on learning, an experiment was conducted involving 100 participants divided into two groups. The experimental group listened to classical music while studying, while the control group studied in silence.
Hypothesis
The hypothesis was that the experimental group would perform better on a memory test administered after the study period.
Variables
- Independent variable:Music (classical music vs. silence)
- Dependent variable:Memory performance
Methodology
The participants were randomly assigned to the experimental or control group. Both groups studied the same material for 30 minutes. After the study period, they completed a memory test consisting of 20 multiple-choice questions.
Data Collection and Analysis
The data from the memory test were analyzed using a t-test. The results showed a significant difference between the two groups, with the experimental group performing significantly better than the control group.
Interpretation of Results
The results of the experiment support the hypothesis that music can enhance memory. The experimental group, who listened to classical music while studying, performed better on the memory test than the control group, who studied in silence.
These findings suggest that music may be a valuable tool for improving learning and memory. By listening to music while studying, students may be able to improve their ability to retain information and perform better on tests.
Recommendations for Future Research: A Student Conducts An Experiment To See How Music
This study provides preliminary evidence for the positive effects of music on learning. Further research is needed to explore the following areas:
- The effects of different types of music on learning
- The optimal duration and frequency of music exposure for learning
- The mechanisms by which music enhances cognitive functions
Question & Answer Hub
What is the main objective of this experiment?
The experiment aims to investigate the effects of music on various cognitive functions, particularly its impact on memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities.
How was the experiment conducted?
The experiment involved a carefully designed methodology, including a specific sample size, participant demographics, and experimental conditions. The data was collected using appropriate methods and analyzed using statistical tests to determine the significance of the findings.
What were the key findings of the experiment?
The analysis of the data revealed significant findings that support the hypothesis, demonstrating the positive impact of music on cognitive functions. The results highlight the potential of music as a tool to enhance learning and academic performance.