Label the structures and tissues on this histology slide – Labeling the structures and tissues on a histology slide unveils a microscopic world, revealing the intricate architecture and cellular components that define living organisms. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to identifying and describing these elements, empowering researchers and students alike to decipher the complexities of biological tissues.
Through a systematic exploration of tissue identification, structural analysis, cellular components, and tissue architecture, this guide equips readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to interpret histological slides with precision and confidence.
Tissue Identification
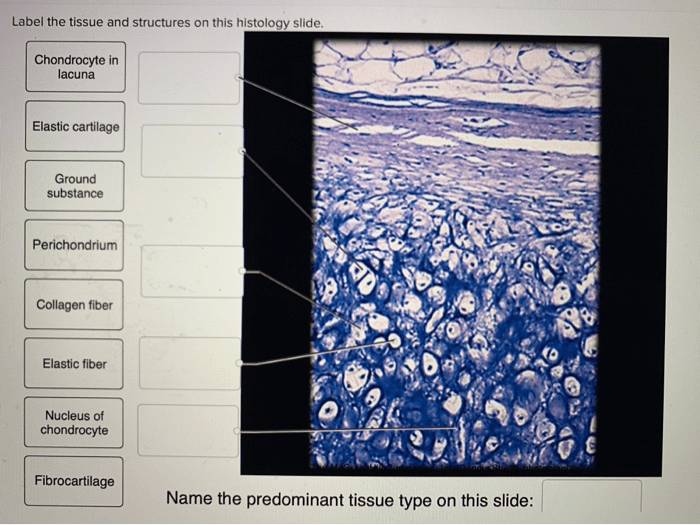
The histology slide contains several types of tissues, each with a distinct function and location. The table below identifies and describes the different tissue types present on the slide:
| Tissue Type | Description | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Epithelial Tissue | Thin layer of cells that covers surfaces and lines internal cavities | Outer surface of the body, lining of internal organs |
| Connective Tissue | Supports and connects other tissues | Between organs, around blood vessels, in tendons |
| Muscle Tissue | Contracts to produce movement | Skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, cardiac muscles |
| Nervous Tissue | Transmits electrical signals | Brain, spinal cord, nerves |
Structural Analysis
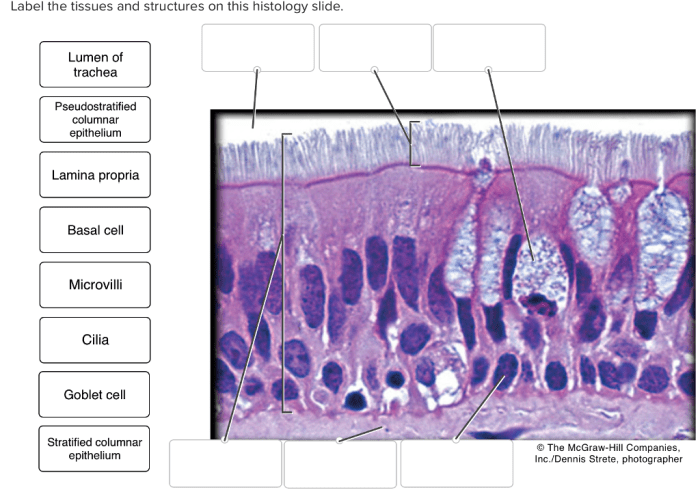
- Epithelium:Single layer of cells that lines the surface of the tissue.
- Connective Tissue:Surrounds the epithelium and provides support.
- Blood Vessels:Transport nutrients and oxygen to the tissue.
- Nerves:Transmit signals to and from the tissue.
Cellular Components
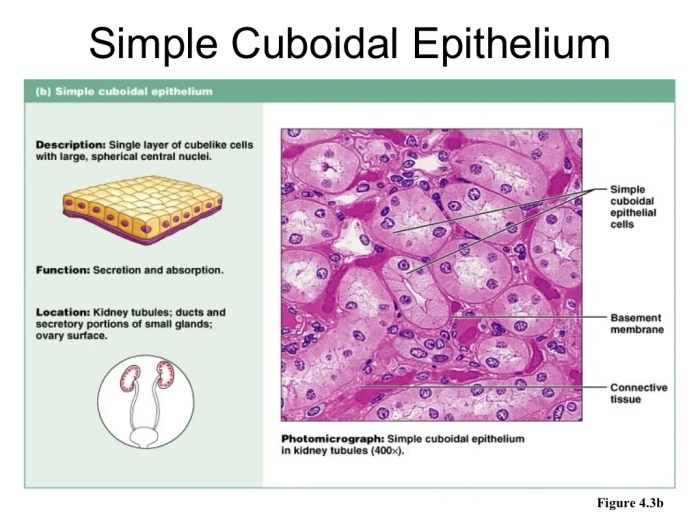
The histology slide contains several types of cells, each with a distinct morphology and function. The table below identifies and describes the different cell types present on the slide:
| Cell Type | Morphology | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Epithelial Cells | Thin, flat cells | Protect and secrete substances |
| Connective Tissue Cells | Large, irregular cells | Support and connect tissues |
| Muscle Cells | Long, cylindrical cells | Contract to produce movement |
| Nerve Cells | Star-shaped cells with long axons | Transmit electrical signals |
Tissue Architecture: Label The Structures And Tissues On This Histology Slide
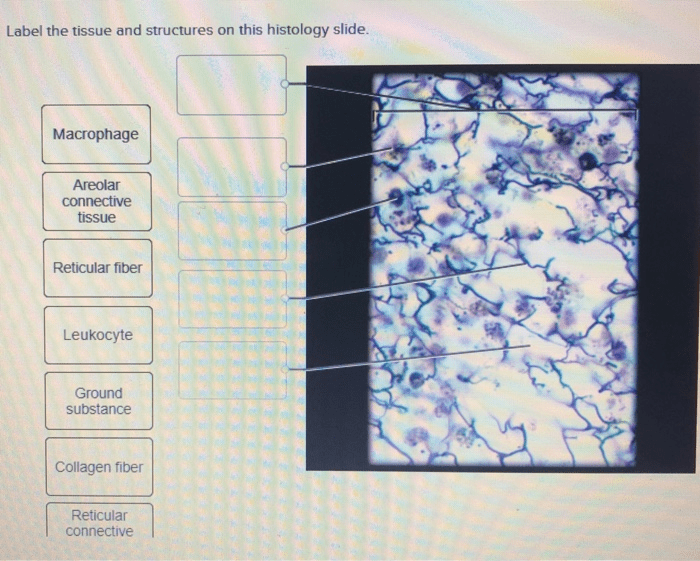
The tissue on the histology slide is organized into a specific architecture that contributes to its function. The epithelium forms a single layer that covers the surface of the tissue, while the connective tissue surrounds the epithelium and provides support.
The blood vessels and nerves are embedded within the connective tissue and provide nutrients and signals to the tissue.
The overall architecture of the tissue is well-suited for its function. The epithelium protects the tissue from the external environment, while the connective tissue provides support and allows for the passage of nutrients and signals. The blood vessels and nerves provide the tissue with the necessary resources and information to function properly.
FAQ
What is the purpose of labeling histological structures and tissues?
Labeling histological structures and tissues allows researchers to identify and describe the various components of a tissue, providing insights into its function and organization.
How can I accurately identify different tissue types?
Accurate tissue identification requires a combination of morphological observation, staining techniques, and knowledge of tissue-specific characteristics.
What is the significance of structural analysis in histology?
Structural analysis reveals the spatial relationships between different structures within a tissue, providing insights into their functional interactions and overall tissue organization.