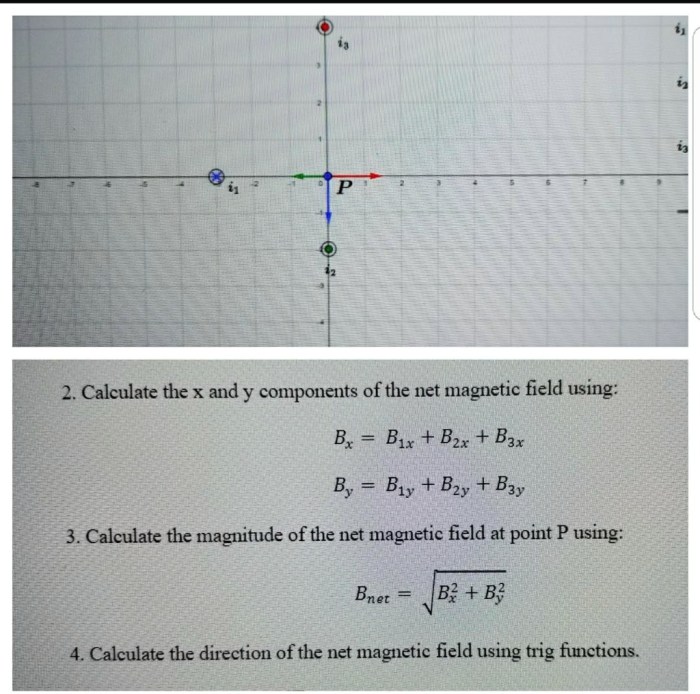
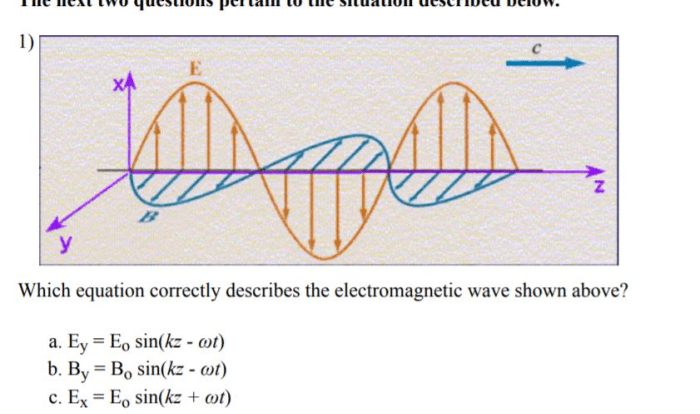
Find the magnitude of magnetic field bnet – Embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of magnetic field magnitude, as we delve into its definition, calculation methods, and practical applications. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the significance of magnetic field magnitude in diverse fields, ranging from electric motors to medical imaging.
Understanding the magnitude of a magnetic field is crucial for comprehending the behavior of magnetic forces and their impact on moving charges. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the complexities of magnetic field magnitude, empowering you to tackle real-world challenges with confidence.
Concepts of Magnetic Field Magnitude

The magnetic field magnitude, denoted by B, is a scalar quantity that describes the strength of a magnetic field at a given point. It represents the force that a magnetic field exerts on a moving charge. The SI unit of magnetic field magnitude is Tesla (T), named after the renowned physicist Nikola Tesla.
The magnetic field magnitude is a fundamental property of magnetic fields and plays a crucial role in various physical phenomena. It is used to characterize the magnetic environment created by magnets, current-carrying conductors, and other sources of magnetic fields.
Units of Magnetic Field Magnitude
The magnetic field magnitude is commonly expressed in Tesla (T) in the International System of Units (SI). One Tesla is defined as the magnetic field strength that exerts a force of one newton on a one-ampere current-carrying conductor one meter long, perpendicular to the magnetic field.
Other units of magnetic field magnitude include:
- Gauss (G): 1 G = 10 -4T
- Oersted (Oe): 1 Oe = (1000/4π) T
- Ampere per meter (A/m): 1 A/m = (4π × 10 -7) T
Methods for Calculating Magnetic Field Magnitude: Find The Magnitude Of Magnetic Field Bnet
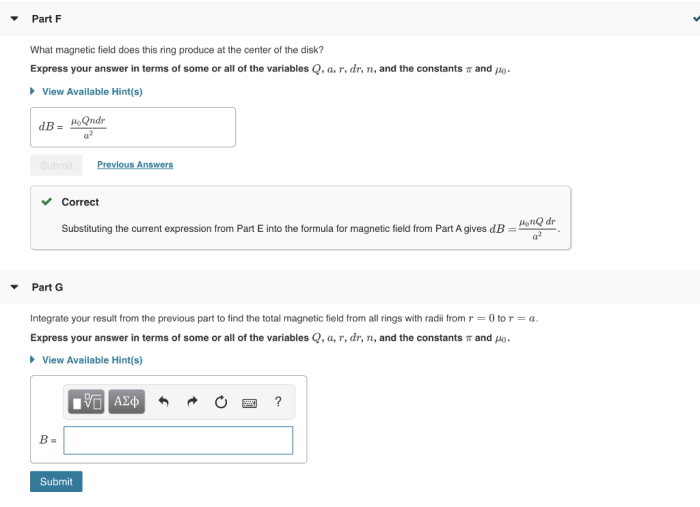
The magnetic field magnitude can be calculated using various methods, depending on the source and geometry of the magnetic field. Two commonly used methods are:
Biot-Savart Law
The Biot-Savart law is a fundamental law in electromagnetism that relates the magnetic field generated by a current-carrying conductor to the current and the shape of the conductor. It states that the magnetic field magnitude at a point due to a current element is proportional to the current, the length of the current element, and the sine of the angle between the current element and the vector from the current element to the point.
Ampere’s Law, Find the magnitude of magnetic field bnet
Ampere’s law is another fundamental law in electromagnetism that relates the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor to the current. It states that the line integral of the magnetic field around a closed loop is equal to the net current passing through the loop multiplied by the permeability of the medium.
Both the Biot-Savart law and Ampere’s law can be used to calculate the magnetic field magnitude in different situations. The choice of method depends on the geometry and symmetry of the current distribution.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the physical significance of magnetic field magnitude?
Magnetic field magnitude represents the strength of a magnetic field at a given point. It determines the force exerted on moving charges and the magnetic torque experienced by magnetic materials.
How can I calculate the magnitude of a magnetic field?
The magnitude of a magnetic field can be calculated using various methods, including the Biot-Savart law and Ampere’s law. These methods involve integrating the contributions from individual current elements or applying symmetry considerations.
What are the practical applications of magnetic field magnitude?
Magnetic field magnitude finds applications in electric motors, generators, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and particle accelerators. It is essential for designing and optimizing these devices to achieve desired performance.